什么是面向对象


回顾方法的定义与调用
方法的定义

import java.io.IOException;//Demo01 类public class Demo01 { //main方法 public static void main(String[] args) { } public String sayHello(){ return "helloWorld"; } public void readFile(String file) throws IOException{ }}方法的调用
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //非静态方法这样 new Student().say(); //或者 Student student=new Student(); student.say(); } //static 的方法是和类一起加载的,存在较早 public static void a(){ // b(); //这里会报错,不能调用!!!!!!! } //类实例化之后才存在 public void b(){ }}//值传递public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a=1; System.out.println(a);//1 change(a); System.out.println(a);//1 } //返回值为空 public static void change(int a){ a=10; }}//引用传递: 传递的对象,本质还是值传递//对象要理解透彻、内存要理解透彻!!!!!!!!public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); System.out.println(person.name);//null change(person); System.out.println(person.name);//wda } public static void change(Person person){ //person 是一个对象:指向的--》Person person = new Person(); 这是一个具体的人可以改变属性 person.name ="wda"; }}//定义了一个Person类,有一个属性class Person{ String name;//null}类与对象的创建


public class Student { //属性;字段 String name;//null int age;//0 //方法 public void study(){ System.out.println(this.name+"在学习"); }}/*public static void main(String[] args) { //类:抽象的,需要实例化 //类实例化后会返回一个自己的对象! Student xiaoming = new Student(); Student xiaohong = new Student(); xiaoming.age=3; xiaoming.name="ming"; System.out.println(xiaoming.name); System.out.println(xiaoming.age); } */构造器详解
package com.oop.demo02;//java-->会生成一个class文件public class Person { //一个类即使什么都不写,也会存在一个方法 //显式的定义构造器 String name; int age; //构造器的功能 //实例化初始值 //1.使用new关键字,本质是在调用构造器 //2.用来初始化值 public Person(){ this.name="safa"; } //有参构造器:一旦定义了有参构造,无参就必须显式定义 public Person(String name){ this.name=name; } //alt+ insert 快捷定义构造器}/*public static void main(String[] args) { //new 实例化了一个对象 Person person = new Person("aaa"); System.out.println(person.name); //aaa } 构造器: 1.和类名相同 2.没有返回值 作用: 1.使用new关键字,本质是在调用构造器 2.用来初始化值 注意点: 1.一旦定义了有参构造,如果想使用无参构造,无参就必须显式定义 alt+ insert 快捷定义构造器 this.= */创建对象内存分析
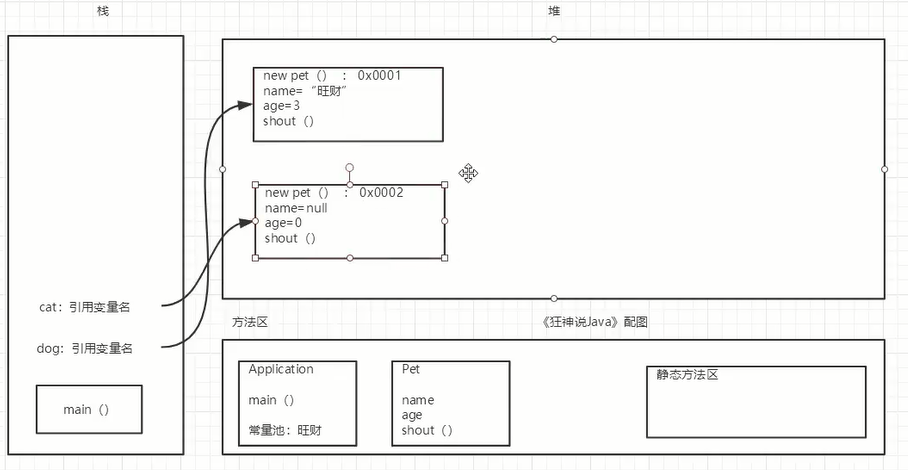
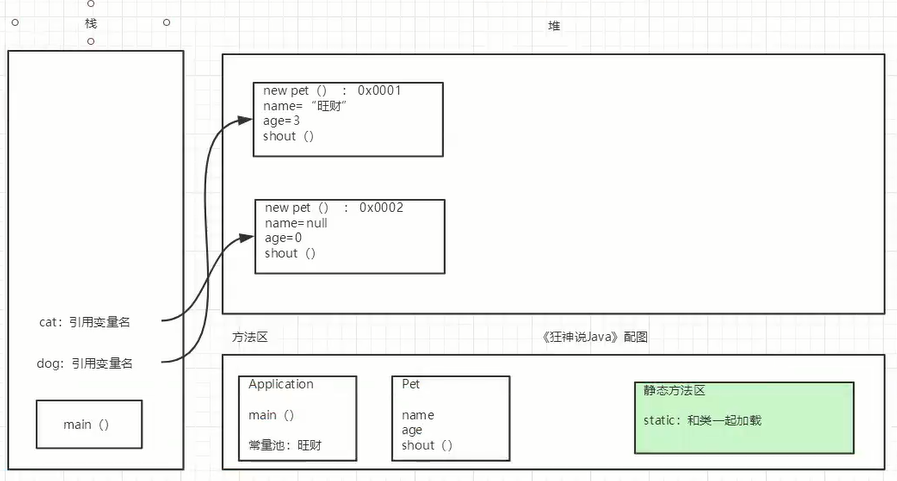
package com.oop.demo03;public class Pet { public String name; public int age; //无参构造 public void shout(){ System.out.println("叫了一声");; }}/*public static void main(String[] args) { Pet dog = new Pet(); dog.name="wangcai"; dog.age=3; dog.shout(); System.out.println(dog.name); System.out.println(dog.age); Pet cat = new Pet(); } */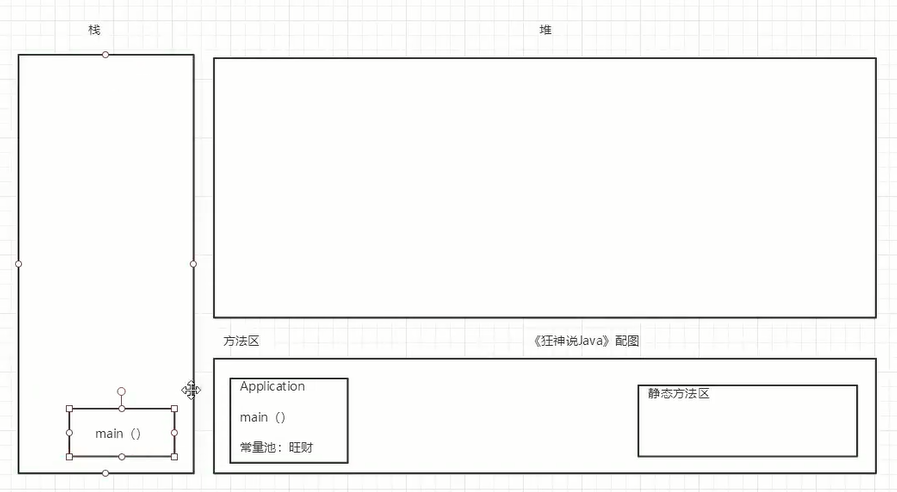



封装详解
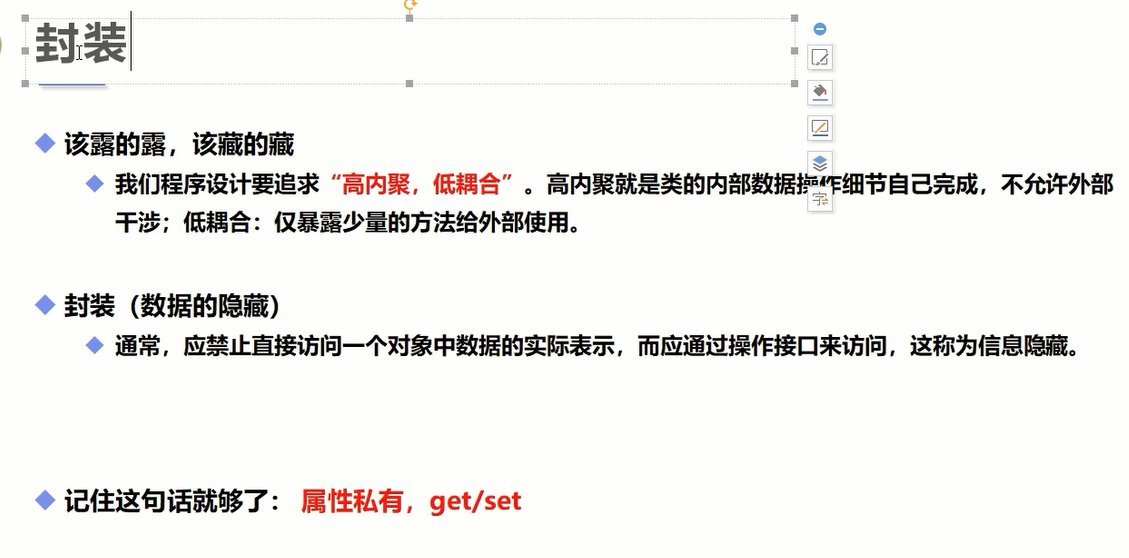
package com.oop.demo04;//private 私有public class Student { //封装大多数时候是对属性来说的,方法里面用的比较少 /* 1.提高程序的安全性 2.隐藏代码的实现细节 3.统一接口 4.系统可维护性增加了 */ // 名字 //属性私有 private String name; //学号 private int id; //性别 private char sex; //年龄 private int age; //提供一些可以操作这个属性的方法 //提供一些pubLicde的get、set方法 //get 获得这个数据 public String getName(){ return this.name; } //set 给这个数据设置值 public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { if(age>120||age<0){ this.age = 3; }else { this.age=age; } } //学习() //睡觉()}/*public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 =new Student(); // s1.name 会报错 s1.setName("sfa"); s1.getName(); //alt + insert 可以智能生成get set!!!!!!!!!! s1.setAge(999);//不合法的 System.out.println(s1.getAge()); } */继承

基础
package com.oop;import com.oop.demo05.Student;public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student =new Student(); student.say(); System.out.println(student.money); //System.out.println(student.money_private); //报错,说明父类私有的属性不能继承 }}package com.oop.demo05;//在Java中,所有的类,都默认直接或间接继承object类//人 父类public class Person /*extends Object*/{ //public //protected //default //private public int money =10_0000_0000; private int money_private=10; public void say(){ System.out.println("说了一句话"); }}package com.oop.demo05;//学生 is 人 派生类//子类继承了父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法!!!public class Student extends Person{ //ctrl+h 打开继承树!!!!!!}package com.oop.demo05;//Teacher is Person 派生类public class Teacher extends Person{}super详解
package com.oop;import com.oop.demo05.Student;public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student =new Student(); //Person无参构造执行了 //Student 无参执行了 //student.test("aa"); student.test1(); }}package com.oop.demo05;//在Java中,所有的类,都默认直接或间接继承object类//人 父类public class Person /*extends Object*/{ //public //protected //default //private public int money =10_0000_0000; private int money_private=10; protected String name="ks"; //public-->private则出错,私有的东西无法继承 public void print(){ System.out.println("person"); } public void say(){ System.out.println("说了一句话"); } public Person() { System.out.println("Person无参构造执行了"); }}package com.oop.demo05;//学生 is 人 派生类//子类继承了父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法!!!public class Student extends Person{ //ctrl+h 打开继承树!!!!!! private String name="qj"; public void test(String name){ System.out.println(name);//aa System.out.println(this.name);//qj System.out.println(super.name);//ks } public void print(){ System.out.println("Student"); } public void test1(){ print();//Student this.print();//Student super.print();//person } public Student() { //隐藏代码,默认调用了父类的无参构造!!!!!!!!!! super();//调用父类的构造器,必须要在子类构造器第一行 System.out.println("Student 无参执行了"); }}super注意点: 1.super调用父类的构造方法,必须在构造方法的第一行 2.super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中! 3.super和this不能同时调用构造方法vs this: 代表的对象不同: this:本身调用者这个对象 super:代表父类对象的应用 前提: this:没有继承也可以使用 super:只能在继承条件才可以使用 构造方法 this();本类的构造 super();父类的构造方法重写
package com.oop.demo05;//继承public class A extends B{ @Override //注解:有功能的注释 public void test() { System.out.println("A->test()"); }}package com.oop.demo05;//重写都是方法的重写,和属性无关public class B { public void test(){ System.out.println("B->test()"); }}package com.oop;import com.oop.demo05.A;import com.oop.demo05.B;public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //静态的方法和非静态的方法区别很大 //静态方法:方法的调用只和左边,定义的数据类型有关 //只有非静态才叫做重写 ,private也不可以,只有public才可以 A a=new A(); a.test(); //父类的引用指向了子类 B b=new A();//子类重写了父类的方法 b.test(); //test()方法都有static时 //A->test() //B->test() //静态的方法和非静态的方法区别很大 //去掉static,即重写之后 //A->test() //A->test() }}重写:需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法! 1.方法名必须相同 2.参数列表必须相同 3.修饰符:范围可以扩大:public>protected>default>private 4.抛出的异常:范围,可以被缩小,但不能扩大;classNotFoundException(xiao)-- Exception(da)是不可以的重写,子类的方法和父类必须要一致,方法体不同为什么需要重写: 1.父类的功能,子类不一定需要,或者不一定满足! 快捷键: Alt+insert :override!!!!!!多态
什么是多态

package com.oop;import com.oop.demo06.Person;import com.oop.demo06.Student;public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //一个对象的实际类型是确定的 //new Student(); //new Person(); //可以指向的引用类型就不确定了: 父类的引用指向子类 //Student 能调用的方法都是自己的或者继承父类的 Student s1 = new Student(); //Person 父类型。可以指向子类,但是不能调用子类独有的方法 Person s2 = new Student(); Object s3 =new Student(); s2.run();//son 子类重写了父类的方法,执行子类的方法 s1.run();//son //对象能执行哪些方法,主要看对象左边的类型,和右边关系不大 // s2.eat(); 报错 ((Student)s2).eat(); s1.eat();//eat }}package com.oop.demo06;public class Student extends Person{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("son"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("eat"); }}/*多态注意事项:!!!!!!!!!!!!!1.多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态2.父类和子类,有联系 否则有类型转换异常 ClassCastException3.存在条件:继承关系,方法需要重写,父类引用指向子类对象 Father f1= new Son(); 1.static 方法,属于类,它不属于实例 2.final 常量,不可以改变 3.private 方法,私有的不能重写 */package com.oop.demo06;public class Person { public void run(){ System.out.println("run"); }}instanceof 和类型转换
package com.oop;import com.oop.demo06.Person;import com.oop.demo06.Student;import com.oop.demo06.Teacher;public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //类型之间的转换:父 子 //高 低 Person obj=new Student(); //student 将这个对象转换为Student类型,就可以使用Student类型的方法了! ((Student) obj).go(); //子类转换为父类,可能丢失自己的本来的一些方法! Student student = new Student(); student.go(); Person person=student; //person.go();//报错 }}/*1.父类引用指向子类的对象2.把子类转换为父类,向上转型:3.把父类转换为子类,向下转型:强制转换4.方便方法的调用,减少重复的代码!简洁!抽象:封装、继承、多态! 抽象类,接口 */package com.oop.demo06;public class Person { public void run(){ System.out.println("run"); }}package com.oop.demo06;public class Student extends Person{ public void go(){ System.out.println("go"); }}/*//System.out.println(X instanceof Y);//能不能编译通过取决于是否有父子关系 //Object>String //Object>Person>Teacher //Object>Person>Student Object object = new Student(); System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);//false System.out.println(object instanceof String);//false System.out.println("============================="); Person person =new Student(); System.out.println(person instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(person instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(person instanceof Object);//true System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher);//false //System.out.println(person instanceof String);//编译报错 System.out.println("============================="); Student student =new Student(); System.out.println(student instanceof Student);//true System.out.println(student instanceof Person);//true System.out.println(student instanceof Object);//true //System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher);//编译报错 //System.out.println(student instanceof String);//编译报错 */package com.oop.demo06;public class Teacher extends Person{}static关键字
package com.oop.demo07;public class Student { private static int age;//静态变量 多线程中会仔细说到 private double score;//非静态变量 public void run(){ } public static void go(){ } public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student(); System.out.println(Student.age);//建议通过这种类型来访问静态变量,静态的变量对于类而言在内存中只有一个,可以被类中所有实例共享// System.out.println(Student.score);//报错 System.out.println(s1.age); System.out.println(s1.score);// Student.run();//报错 new Student().run(); Student.go(); go();//类中的的方法可以直接访问类中的静态方法 }}package com.oop.demo07;public final class Person { //被final修饰的类不能被继承 { //匿名代码块 //程序执行时不能主动调用这个代码块 //创建对象时自动创建,而且在构造器之前 //可以用来赋初值 System.out.println("匿名代码块"); } static{ //静态代码块 //类一加载就直接执行 //永久执行一次 System.out.println("静态代码块"); } public Person() { System.out.println("构造方法"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Person person1=new Person(); System.out.println("=============="); Person person2=new Person(); /* 静态代码块 匿名代码块 构造方法 ============== 匿名代码块 构造方法 */ }}package com.oop.demo07;//静态导入包import static java.lang.Math.random;import static java.lang.Math.PI;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(random()); System.out.println(PI); }}抽象类

package com.oop.demo08;//抽象类 extends: 单继承~ (接口可以实现多继承)例如插座~public abstract class Action { //约束~有人帮我们实现 //抽象方法,只有方法名字,没有方法的实现 public abstract void doSomeThing(); //1.不能new这个抽象类,只能靠子类去实现它;约束! //2.抽象类中可以写普通方法 //3.抽象方法必须在抽象类中 //抽象的抽象:约束 //思考题 不能new,存在构造器吗? 存在!!!!↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓ //存在的意义是什么 抽象出来 提高开发效率 public Action() { }}//抽象类的所有方法,继承了它的子类,都必须实现这些方法~除非~它也是抽象类public class A extends Action{ @Override public void doSomeThing() { }}接口的定义与实现

package com.oop.demo09;//抽象的思维~Java 架构师~//interface 定义的关键字,接口都需要有实现类public interface UserService { //接口中的所有定义的方法其实都是抽象的 默认为public abstract //属性都是常量 默认 public static final int AGE=99; void add(String name); void delete(String name); void uodate(String name); void query(String name);}package com.oop.demo09;public interface TimeService { void timer();}package com.oop.demo09;//抽象类:extends//类可以实现接口//实现了接口的类,就需要重写接口中的方法//多继承,利用接口实现多继承public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService,TimeService{ @Override public void add(String name) { } @Override public void delete(String name) { } @Override public void uodate(String name) { } @Override public void query(String name) { } @Override public void timer() { }}作用: 1.约束 2.定义一些方法,让不同的人实现~ 10----》1 3.方法都是 public abstract 4.属性都是 public static final 5.接口不可以实例化~,接口中没有构造方法 6.implements可以实现多个接口 7.必须重写接口中的方法~内部类

package com.oop;import com.oop.demo10.Outer;public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Outer outer = new Outer(); //通过这个外部类来实例化内部类 Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner(); inner.getID();//10 }}package com.oop.demo10;public class Outer { private int id=10; public void out(){ System.out.println("这是外部类的方法"); //局部内部类 class Inner{ public void in(){ } } } public class Inner{ public void in(){ System.out.println("这是内部类的方法"); } //获得外部类的私有属性~ public void getID(){ System.out.println(id); } } //静态内部类 public static class Inner2{ public void in(){ System.out.println("这是内部类的方法"); } //不能获得外部类的属性 public void getID(){// System.out.println(id);//报错 } }}//一个Java类中可以由多个class类,但是只能由public classclass A{}package com.oop.demo10;public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Apple apple = new Apple(); //没有名字初始化类,不用将实例保存在变量中 new Apple().eat(); //没有名字初始化接口 new UserService(){ @Override public void hello() { } }; }}class Apple{ public void eat(){ System.out.println("1"); }}interface UserService{ void hello();}原文转载:http://www.shaoqun.com/a/607576.html
taofenba:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1725
dojo:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2052
什么是面向对象回顾方法的定义与调用方法的定义importjava.io.IOException;//Demo01类publicclassDemo01{//main方法publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){}publicStringsayHello(){return"helloWorld";}publicvoidreadFile(Stringfil
patpat:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1079
声网agora:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2176
聚贸:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1305
上周发生的电商圈大事,你想知道的都在这儿了!!:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/109869
危险玩具高达1/5,平台甩锅给卖家怕是行不通了!:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/111308
电商ROI到底指什么?计算公式及理论详解:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/96299
No comments:
Post a Comment